How to avoid overtraining – the best tips

Anyone who knows a little about fitness training knows: It takes certain stimuli to trigger the desired effects in the body. But those who constantly push their limits or even exceed their borders do themselves no favor. But if you know what is going on in your body during training, you can avoid overtraining.
Overtraining and the theory of supercompensation
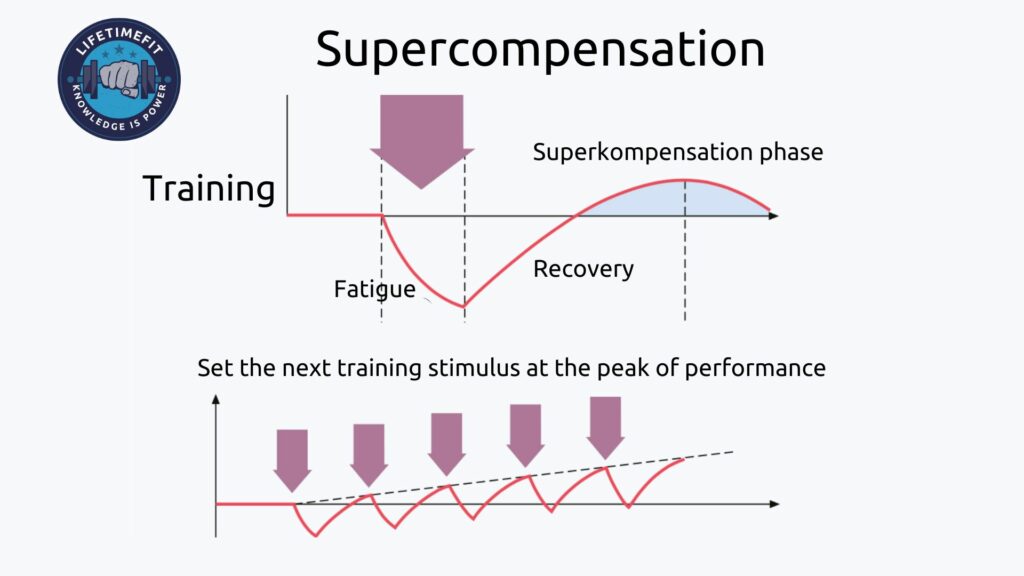
At first, it sounds paradoxical: If you want to improve your fitness and performance, you must systematically weaken yourself. But a closer look at your body shows what that meant. After every workout, something happens with your body, what experts call supercompensation. Moreover, this supercompensation plays a vital role in connection with overtraining.
- Due to sufficiently intensive training, it comes to a deliberate disturbance of your biological balance. Proteins play an essential role in this process.
- The body gets tired and the athletic performance decreases during the training.
- Immediately after the end of the training, the organism starts the recovery phase. Our intelligent body wants to be better prepared for the next workout and reacts with adaptation symptoms.
- Bone density increases, creating new small blood vessels. New mitochondria are also formed. These power stations of the cells provide more energy.
- The bone density increases and new small blood vessels are formed. They supply the body with more blood and oxygen. New mitochondria are also created. These power stations of the cells provide more energy.
Too short recovery provokes overtraining
The next training stimulus should occur at the peak of these adaptation symptoms. However, this intelligent system only works if you give your body enough time to regenerate. If you strain yourself too early, you risk overtraining. If you wait too long, you will start all over again because the effect will not occur.
How long does regeneration take
So if you want to increase your performance continuously, you need to know how long your body needs to recover after a workout:
- Creatine phosphate is a high-speed energy supplier that reacts within a few minutes.
- Glycogen storage takes several hours.
- Muscle cells can take several days to recover. This depends on the intensity of the training.
The body needs this time
The recovery time depends on your performance. Top athletes have a much shorter recovery period because they have been training for many years. For all other athletes and fitness enthusiasts, sports science relies on experience to avoid overtraining:
- After an aerobic workout, like moderate jogging, swimming, cycling, or inline skating, the body needs eight to twelve hours.
- The body needs 24 to 48 hours to recover after anaerobic training like interval training or HIIT.
- After intensive strength training, the body and especially the muscles need 48 to 72 hours.
You can learn to listen to your body
As said, the recovery times are a matter of experience. If you train longer and regularly you learn to listen to your body’s signals. Eventually will be able to estimate how long it will take to recover from a workout. Good coaches can also estimate that.
These symptoms can be associated with overtraining
Important to know: Not only do the sporting factors play a role in overtraining but also the psychological factors. These include high workloads, stress in a relationship, or other stressful events such as illness or the death of a loved one. The following symptoms are typical of overtraining:

Go to the doctor
If you experience a noticeable drop in performance and you have no explanation for it, you should consult a doctor. The main aim of the examination should be to rule out any illness.
1 thought on “How to avoid overtraining – the best tips”